What Is The Dark Web And Why Is It A Threat to SMEs?
March 15, 2024
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so do the threats that businesses face. Among the various facets of cyber security, dark web monitoring emerges as a critical, yet often overlooked, component in safeguarding business interests. However, for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), the significance of the dark web may not be immediately apparent.

In this blog, we’ll delve into the depths of the dark web, shedding light on its nature, its uses, and most importantly, the substantial risks it poses to SMEs. By gaining a deeper understanding of this shadowy corner of the internet, SMEs can adopt proactive measures to protect their digital assets and ensure the security of their businesses.

The internet is expansive, hosting millions of web pages, databases, and servers that are active 24/7. However, what we commonly interact with as the “visible” internet, known as the surface web, barely scratches the surface. These are the websites easily accessible through search engines like Google and Yahoo. Beneath this visible layer lies a concealed realm—the deep web and the dark web. Experts suggest that 96% of the internet remains hidden, with 90% comprising the deep web and the remaining 6% constituting the darkest segment, the dark web.
Watch our quick video to learn about the dangers of the dark web.

This is the part of the internet that’s visible and easily accessible, making up less than 4% of the total web. You can find it using standard browsers like Google Chrome. Websites here usually end with “.com” or “.org” and are indexed by search engines through visible links.
The deep web lies beneath the surface and remains unindexed by search engines. It encompasses all content not accessible through standard search engines, including email services, databases, private intranets, and the dark web.
Though often conflated, the deep web and dark web are distinct. Much of the deep web is legal and secure, encompassing sensitive financial and medical data, among other protected content. Accessing the deep web is part of everyday internet use, including password-protected pages and those deliberately excluded from search engine indexes.
The Dark Web is a hidden section of the internet, comprising a network of encrypted sites intentionally concealed from public view. Unlike the surface web, it is not indexed by search engines and can only be accessed with specialised software like the Tor network.
Often associated with criminal activities, the Dark Web facilitates anonymous communication and transactions, posing significant threats to SMEs. Cybercriminals exploit its anonymity to trade stolen data, malware, and hacking tools.
Its construction prioritises anonymity, with features including:
Now that you understand the dark web, you may wonder about its purposes. The dark web’s anonymity fosters illegal activities, attracting criminal elements. Its accessibility challenges and high entry barriers facilitate various illicit transactions.
Users on the dark web engage in transactions involving stolen credit card numbers, personal information, streaming service credentials, illegal content like child sexual abuse material, counterfeit currency, and tools for cybercrimes such as ransomware attacks. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are frequently employed for anonymous e-commerce transactions on the dark web.
Despite its notorious reputation, the dark web itself is not inherently illegal and serves legitimate purposes. It provides a communication platform in restricted environments and aids political activists and journalists. Additionally, it hosts unique content such as banned literature and discussion forums.
Law enforcement agencies and cyber threat intelligence specialists utilise the dark web to gather intelligence on cyber threats and illegal activities. Their efforts are vital in safeguarding organisations of all sizes, governments, and the public from cyber threats and criminal activities.
The Dark Web serves as a marketplace for cybercriminals to trade stolen data, allowing them to profit from their illicit activities. SMEs across all industries are common targets for cybercriminals. They store valuable information such as customer, financial, and employee records, making them attractive to malicious actors. The pie chart below, sourced from Kroll’s Data Breach Outlook 2024 report, illustrates the pervasive nature of data breaches across all industries.
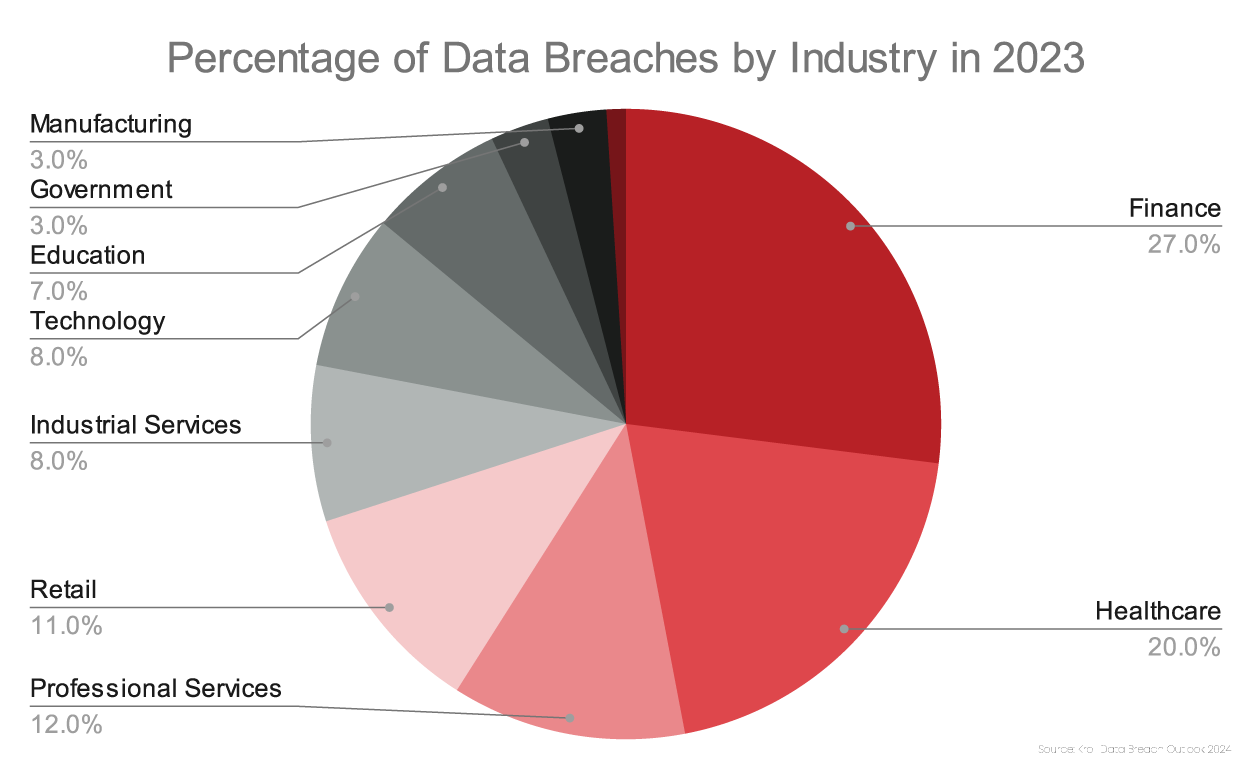
In recent years, cyberattacks against businesses have surged, with SMEs increasingly becoming attractive targets. Notably, certain types of attacks, such as social engineering attacks like phishing, are more frequently directed at small businesses.

SMEs face heightened vulnerability to data breaches due to limited resources allocated to cyber security measures. Once their business information is compromised and traded on the Dark Web, it becomes susceptible to identity theft, fraud, and other criminal activities. Furthermore, SMEs may lack awareness of the risks associated with the Dark Web, exacerbating their susceptibility to attacks.
The Dark Web serves as a marketplace for stolen data, where cybercriminals trade valuable information like credit card details and login credentials. This data is often acquired through phishing scams, malware attacks, and brute force tactics. This illicit trade allows nefarious actors to exploit the data for unlawful purposes. They leverage the anonymity of the Dark Web to evade detection and enforcement efforts.
Moreover, a sizeable portion of data stolen during security breaches eventually finds its way onto the Dark Web. This data is available for purchase at remarkably low prices, as demonstrated by the Privacy Sharks Dark Web Price Index 2024.

This accessibility and affordability of sensitive data underscore the significant role the Dark Web plays in facilitating data breaches and cybercrime.
Real-life examples underscore the critical importance of Dark Web monitoring. These instances highlight the substantial risks of data breaches on the Dark Web. They underscore the urgent need for proactive measures to protect sensitive information and minimise potential damages.
In January 2024, a security researcher, Bob Diachenko, discovered a massive database containing 26 billion leaked records, affecting millions or even billions of individuals. Dubbed the “Mother of All Breaches,” this incident is believed to be the largest breach in history.
The dataset includes information from various global social media platforms and online services. The database comprises re-indexed leaks, breaches, and privately sold databases. Notable contributors include Tencent, Weibo, MySpace, and X, alongside organisations like Adobe, Dropbox, LinkedIn, and Telegram, among others.
Researchers suspect that an initial access broker compiled the data from multiple sources to profit on the dark web. This data could be used for various malicious activities, including identity theft, phishing, and business email compromise.
In June 2021, data associated with 700 million LinkedIn users was posted on a dark web forum, affecting over 90% of its user base. A hacker named “God User” used data scraping techniques to exploit LinkedIn’s API. This resulted in the exposure of email addresses, phone numbers, geolocation records, genders, and other social media details.
While LinkedIn argued that no sensitive personal data was exposed, the incident violated its terms of service. The leaked data provided malicious actors with ample information to execute convincing social engineering attacks.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. The Dark Web is a growing threat to SMEs, with its clandestine nature facilitating illicit activities. This poses dire consequences for businesses and their clientele. Every moment counts; companies must bolster their cyber defences by extending their surveillance beyond the Surface Web to encompass the Dark Web. Failure to act promptly could expose your company’s and customers’ sensitive information, leaving your bank accounts, emails, and other online assets vulnerable to exploitation.
Our comprehensive Dark Web monitoring services offer a vital lifeline. By leveraging our innovative technology and expertise, we can detect and thwart potential breaches before they materialise, safeguarding your SME against the perils of the Dark Web. Don’t delay any further – contact us today to fortify your defences and ensure the security of your business data in the face of the Dark Web menace.

Contact us to learn more about our cyber security solutions, request a consultation, or share your thoughts on our blog content. We’re here to assist you in protecting your business from evolving cyber threats.
Call us +44 20 8126 8620
Email us [email protected]
"*" indicates required fields